Gout is an ancient and modern disease, which is both an imperial disease in ancient times and a civilization disease in contemporary times. The cause of patients' illness is often related to their lifestyle habits, especially in terms of diet. If you don't pay attention when eating, gout may come to you. So, which foods or lifestyles are prone to trigger gout, and what harm can gout bring to the human body?
Gout is more common in middle-aged men, accounting for only 5% of women, mainly postmenopausal women, and there is a trend of younger onset of gout. The natural course of gout can be divided into four stages, namely asymptomatic hyperuricemia stage, acute stage, intermittent stage, and chronic stage. The clinical manifestations are as follows:
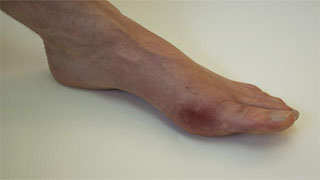
1. Acute gouty arthritis
Most patients have no obvious symptoms before the onset, or only fatigue, general discomfort, and joint pain. A typical episode often wakes up late at night due to joint pain, which progressively intensifies and reaches its peak around 12 hours, presenting as tearing, cutting, or biting, and is unbearable. Affected joints and surrounding tissues are red, swollen, hot, painful, and functionally restricted. Relieve on its own within a few days or 2 weeks.
The first episode often involves a single joint, with some cases occurring in the first metatarsophalangeal joint. In the later course of the disease, some patients may also involve this area. Secondly, joints such as the dorsum, heel, ankle, knee, wrist, and elbow are less affected, while joints such as the shoulder, hip, spine, and temporomandibular joint are less affected. Multiple joints can be affected simultaneously, resulting in polyarthritis. Some patients may have systemic symptoms such as fever, chills, headache, palpitations, and nausea, accompanied by increased white blood cell count, faster erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and elevated C-reactive protein.
2. Intermittent seizure period
Gout attacks last for several days to weeks and can be relieved on their own. Generally, there are no obvious residual symptoms, or local skin pigmentation, flaking, and itching. Afterwards, they enter an asymptomatic interval and recur after several months, years, or more. Most patients relapse within one year, becoming more frequent and affecting more and more joints. The duration of symptoms becomes longer and longer, and the affected joints generally develop from the lower limbs to the upper limbs, and from distal small joints to large joints. Joint involvement may occur in the fingers, wrists, elbows, and other joints. A few patients may affect the shoulder, hip, sacroiliac, sternoclavicular, or spinal joints, as well as the surrounding bursae, tendons, and tendon sheaths. Symptoms tend to be atypical. A small number of patients have no rest period and present with chronic arthritis symptoms after the initial onset.
3. Chronic gouty tophus lesion stage
Subcutaneous gouty tophi and chronic gouty tophus arthritis are long-term and significant hyperuricemia, resulting in the deposition of large amounts of monosodium urate crystals under the skin, joint synovium, cartilage, bone, and soft tissues around the joints.
The typical site of subcutaneous gouty tophi is the earlobe, and it is also commonly found around recurrent joints and in areas such as the olecranon, Achilles tendon, and patellar bursa. The appearance is yellow white growths of varying sizes that protrude subcutaneously, with a thin skin surface. After rupture, white powder or paste like substances are discharged, which persist for a long time without healing.
Subcutaneous gouty tophi often coexist with chronic gouty tophaceous arthritis. The large deposition of gouty tophi in joints can cause joint bone destruction, fibrosis of surrounding tissues, and secondary degenerative changes. The clinical manifestations include persistent joint pain, tenderness, deformity, and functional impairment. The symptoms during the chronic phase are relatively mild, but there may also be acute attacks.
4. Renal lesions
(1) Chronic urate nephropathy involves the deposition of urate crystals in the renal interstitium, leading to chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis. Clinical manifestations include decreased urine concentration function, increased nocturia, low specific gravity urine, small molecule proteinuria, white blood cell urine, mild hematuria, and tubular urine. Late stage can lead to a decrease in glomerular filtration function, resulting in renal dysfunction.
(2) Uric acid urinary tract stones have an increased concentration of uric acid in the urine, which is in a supersaturated state and deposits in the urinary system, forming stones. The incidence rate in gout patients is over 20%, and it may occur before the onset of gouty arthritis. For those with smaller stones, they appear gravel like and can be excreted with urine without symptoms; Larger cases can block the urinary tract, causing renal colic, hematuria, difficulty urinating, urinary tract infections, renal pelvis dilation, and hydronephrosis.
(3) Acute uric acid nephropathy results in a sudden increase in blood and urine uric acid levels, with a large amount of uric acid crystals depositing in the renal tubules, collecting ducts, and other areas, causing acute urinary tract obstruction. Clinical manifestations include oliguria, anuria, and acute renal failure; A large amount of uric acid crystals can be seen in the urine. It is often caused by secondary factors such as malignant tumors and their radiation and chemotherapy (i.e. tumor lysis syndrome).
Gout is not a disease, it heralds a series of chronic illnesses. If you have gout, please check if you are also suffering from the above-mentioned diseases and detect and treat them as soon as possible. If not detected, it can also be prevented as early as possible.
1. Take care of your feet
Keeping feet warm is a way to nourish the kidneys. This is because the kidney meridian originates from the soles of the feet, which are easily invaded by cold air. Therefore, special attention should be paid to keeping the feet warm, and do not face the air conditioner or fan directly when sleeping; Do not walk barefoot in damp places for a long time.
In addition, there are many acupoints on the soles of the feet, such as the Yongquan acupoint. The kidneys originate from gushing springs, and those who are gushing springs also have feet and hearts. Before going to bed every night, you can massage the gushing spring points on the soles of your feet, which can have the effect of nourishing the kidneys and consolidating essence.
2. The stool should be unobstructed
Poor bowel movements, stagnant stool, and rising turbid qi can not only cause restlessness and shortness of breath, but also damage the kidneys, leading to lower back pain, fatigue, nausea, and vomiting. Therefore, maintaining smooth bowel movements is also a way to nourish the kidneys.
When it is difficult to defecate, you can use both hands and backs of your hands to press and massage the kidney area vigorously, which can stimulate kidney qi and accelerate defecation; When walking, massaging the kidney area with both hands can alleviate symptoms of lower back pain.
3. Drinking water to nourish the kidneys
Water is the source of life. Insufficient water may cause the retention of turbid toxins and increase the burden on the kidneys. Therefore, drinking water regularly is an important way to nourish the kidneys.
4. Don't hold back when you have urine
When the urine stored in the bladder reaches a certain level, it will stimulate the nerves and produce a urinary reflex. At this time, it is necessary to go to the toilet in a timely manner and discharge the urine completely. Otherwise, the accumulated urine will become cloudy and harmful to the kidneys. Therefore, timely excretion of urine is also one of the best ways to nourish the kidneys.
5. Swallowing saliva to nourish the kidneys
The saliva in the mouth is divided into two parts: clear and sparse saliva, which is controlled by the spleen; Thick is saliva, controlled by the kidneys. You can conduct an experiment where you spit out saliva as soon as you have it in your mouth. In less than a day, you will feel weak and tired in your waist. This in turn proves that swallowing body fluids can nourish kidney essence and play a role in protecting the kidneys.
6. Diet protects the kidneys
There are many foods that can nourish the kidneys. In addition to black foods such as black sesame, black fungus, black rice, and black beans that can nourish the kidneys, walnuts, chives, shrimp, and lamb loin can also have a kidney nourishing effect.
7. Sleep nourishes the kidneys
Adequate sleep plays an important role in the biochemistry of qi and blood, as well as the maintenance of kidney essence. Clinical findings have shown that many patients with renal failure experience excessive staying up late, excessive fatigue, and lack of sleep. Therefore, do not stay up too late, develop good sleep habits, go to bed early and wake up early, which is beneficial for the maintenance of kidney essence.
(1) Clearing heat and accumulating gout
Symptoms: Local joint redness, swelling, heat and pain, sudden onset, affecting one or more joints, often accompanied by fever, chills, thirst, restlessness or headache, sweating, short yellow urine, red tongue with yellow coating, or yellow and greasy, and smooth pulse.
Treatment principles and methods: clearing heat and dampness, unblocking collaterals and relieving pain.
Prescription: San Miao San combined with Danggui Niantong Tang, modified. Stir fried Atractylodes macrocephala, Sichuan Phellodendron, Sichuan Achyranthes, Artemisia scoparia, Qianghuo, Duhuo, Angelica sinensis, Ligusticum chuanxiong, Polygonum cuspidatum, Windproof, Self Defense, Poria cocos, Poria cocos, and Alisma.
(2) Cold dampness obstruction type gout
Symptoms: Joint pain, mild swelling, local fever, localized pain, difficulty in flexion and extension, or subcutaneous nodules or gouty stones, numb skin, thin white or greasy tongue coating, stringy or slow pulse.
Treatment principles and methods: Warm meridians to dispel coldness, dehumidify and unblock collaterals.
Prescription: Modified Aconitum Decoction. Chuanwu, Ephedra sinica, Astragalus membranaceus, Paeonia lactiflora, Atractylodes macrocephala, Atractylodes macrocephala, Radix Notopterygii, Curcuma longa, Angelica sinensis, Poria cocos, Polygonatum sibiricum, Licorice.
(3) Phlegm stasis obstruction type gout
Symptoms: Recurrent joint pain that persists for a long time, sometimes mild and sometimes severe, or presenting as stabbing pain, fixed without moving, joint swelling, and even stiffness and deformity, poor flexion and extension, subcutaneous nodules, or skin color that is purple dark, with veins that are stringy or dull.
Treatment principles and methods: promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis, resolving phlegm and dispersing nodules.
Prescription: Taohong Siwu Tang combined with Danggui Niantong Tang, modified. Quan Danggui, Chuanxiong, Chishao, Taoren, Yinchen, Weilingxian, Haifengteng, Zhuling, Fuling, Jinqiancao, Tufuling, and Bixie.
(4) Spleen deficiency and dampness obstruction type gout
Symptoms: Asymptomatic period, or only mild joint symptoms, or hyperuricemia, or physical fatigue, dizziness, lower back and knee pain, reduced appetite, abdominal distension and tightness, pale and plump tongue or red tongue tip, white or yellow thick and greasy coating, fine or smooth pulse, etc.
Treatment principles and methods: invigorate the spleen and eliminate dampness, nourish qi and unblock collaterals.
Prescription: Huangqi Fangji Tang, modified. Huangqi, Fangji, Guizhi, Xixin, Danggui, Duhuo, Qianghuo, Atractylodes macrocephala, Fangfeng, Epimedium, Paeonia lactiflora, Poria cocos, Bixie, Licorice.


